中国组织工程研究 ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (21): 3412-3419.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.21.023
• 生物材料综述 biomaterial review • 上一篇 下一篇
用于心血管医疗装置的聚合物材料表面构建与生物相容性研究Ⅱ-心血管医疗装置聚合物的表面构建与生物反应行为
陈宝林1,王东安2,3
- 1呼伦贝尔学院科研处,内蒙古自治区呼伦贝尔市 021008;2浙江大学高分子科学研究所,浙江省杭州市 310027;3 Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis, Tennessee 38163
-
出版日期:2014-05-21发布日期:2014-05-21 -
作者简介:陈宝林,男,1960年生,河北省新城县人,汉族,1983年东北师范大学毕业,教授,主要从事组织工程材料(生物医用高分子材料)的制备及表征方面的研究。
Phase II study on surface construction and biocompatibility of polymer materials as cardiovascular devices: surface construction and biological responses
Chen Bao-lin1, Wang Dong-an 2, 3
- 1 Bureau of Scientific Research, Hulunbuir College, Hulunbuir 021008, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China
2 Institute of Polymer Science, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310027, Zhejiang Province, China
3 Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis, Tennessee 38163, USA
-
Online:2014-05-21Published:2014-05-21 -
About author:Chen Bao-lin, Professor, Bureau of Scientific Research, Hulunbuir College, Hulunbuir 021008, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
背景:用于心血管医疗的生物材料在血液接触性条件下必须具有抗血栓性、对抗生物降解性与抗感染性。 目的:研制用于心血管组织工程的新型植(介)入型聚合物材料(表面),从聚合物生物材料的表面构建与生物反应行为方面考察各种相应改性表面的生物相容性、血液相容性和细胞相容性。 方法:检索1984至2013年PubMed数据库及万方数据库,英文检索词为“Biocompatibility, Blood compatibility, Biomedical Materials, Biomedical polymer materials”,中文检索词为“生物相容性材料;血液相容性材料;生物医用材料;医用高分子材料”。 结果与结论:通过对蛋白质吸附、细胞黏附中的生物识别、凝血与纤溶过程中的酶催化作用“瀑布模型”,以及生物材料表面构建与蛋白质表面吸附行为4个方面的归纳分析,研制用于心血管组织工程的新型植(介)入型聚合物材料(表面)关键在于对聚合物生物材料生物功能性表面的构建,以及对其相应生物相容性与内皮细胞相容性的研究。通过对聚合物生物材料种类与应用及其心血管医疗器件和可植入性软组织替代物的深入研究可以发现,表面与本体的差别将体现在从表面向本体延伸的很多层分子上,而两种主要因素决定了其包括本体/表面差异及表面相分离在内的本体/表面行为,即表面能和分子运动性。如果考虑到对本体-表面组成差异的理解,还必须追加附加决定因素,即各组分的结晶行为。
中图分类号:
引用本文
陈宝林,王东安. 用于心血管医疗装置的聚合物材料表面构建与生物相容性研究Ⅱ-心血管医疗装置聚合物的表面构建与生物反应行为[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2014, 18(21): 3412-3419.
Chen Bao-lin, Wang Dong-an. Phase II study on surface construction and biocompatibility of polymer materials as cardiovascular devices: surface construction and biological responses[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(21): 3412-3419.
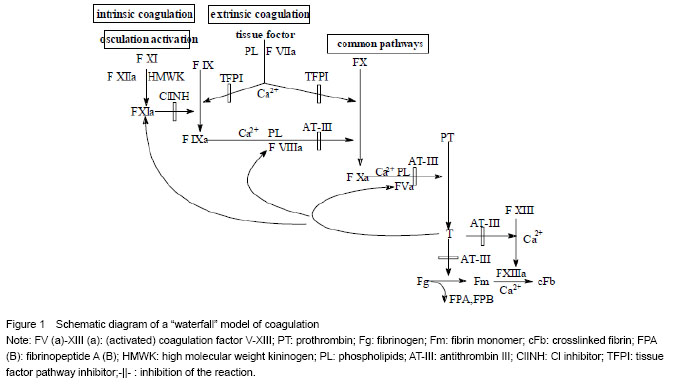
“Waterfall” model of enzyme catalysis during coagulation and fibrinolysis
| [1]Boretos JW, Eden M. Contemporary Biomaterials: material and host response, clinical applications, new technology, and legal aspects. Park Ridge, NJ: Noyes Publications, 1984: 232-233. [2]Chen BL, Wang DA. Surface construction and biocompatibility of polymeric used for cardiovascular medical device. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu. 2013;17(34):6183-6292. [3]Chen BL, Wang DA. Hemocompatibility of biomedical polymeric materials Design of anticoagulant materials. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu. 2012;16(34): 6393-6396. [4]Chen BL, Wang DA. Preparation and mechanism of anticoagulatent biomedical polymer materials with blood compatibility. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2011;15(29):5507-5510. [5]Chen BL, Wang DA, Feng LX. Investigation on methods of surface modification of tissue engineering materials: Polymer surface group transformation and bioactive molecule immobilization. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2010;14(3):552-554. [6]Chen BL, Wang DA, Feng LX. Surface modification of tissue-engineered materials Plasma and grafting modification. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2009;13(3):587-590. [7]Chen BL, Wang DA, Feng LX. Application of polymer biomaterials in the tissue engineering. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2008;12(6): 1189-1192. [8]Chen BL, Wang DA, Feng LX. Polymer porous membrane prepared using thermally induced phase separation. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2007;11(40):8217-8219. [9]Chen BL, Wang DA, Feng LX. Topology of tissue engineered material surface for cell compatibility. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2007;11(18): 3653-3656. [10]Chen BL, Wang DA, Feng LX. Effects of physical-chemical properties of tissue engineered material surface on cell compatibility. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2007;11(1):197-200. [11]Chen BL, Wang DA, Feng LX. Cytological effect of tissue engineering materials with cell compatibility. Zhongguo Linchuang Kangfu. 2006;10(45):225-227. [12]Chen BL, Wang DA, Feng LX, et al. The application of biomedical tissue engineering and the polymer tissue engineering material. Gaoshi Like Xuekan. 2007;27(1):24-26. [13]Chen BL, Wang DA, Feng LX, et al. Study on the blood compatibility of biomedical ploymer materials--project of antithromboeicity materials. Suihua Xueyuan Xuebao. 2007;27(1):186-188. [14]Chen BL, Wang DA, Feng LX. Study on surfaces modify of the tissue engineering materials and application in the tissue engineering. Hulunbeier Xueyuan Xuebao. 2007;15(1):52-54. [15]Chen BL, Wang DA, Feng LX. Study on the tissue compatibility of biomedical ploymer materials--project of tissue-compatibility materials. Hulunbeier Xueyuan Xuebao. 2006;14(6):34-36. [16]Wang DA, Chen BL, Ji J, et al. Selective adsorption of serum albumin on biomedical poiyurethanes modified by a poly(ethylene oxide)coupling-polymer with cibacron blue(F3G-A) end groups. Bioconjug Chem. 2002;13(4): 792-803. [17]Peppas NA, Langer R. New challenges in biomaterials. Science. 1994; 263(5154):1715-1720. [18]Horbett TA, Lew KR. Residence time effects on monoclonal antibody binding to adsorbed fibrinogen. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 1994;6(1):15-33. [19]Chinn JA, Posso SE, Horbett TA, et al. Postadsorptive transitions in fibrinogen adsorbed to polyurethanes: changes in antibody binding and sodium dodecyl sulfate elutability. J Biomed Mater Res. 1992;26(6):757-778. [20]Hynes RO. Integrins: versatility, modulation, and signaling in cell adhesion. Cell. 1992;69(1):11-25. [21]Buck CA, Horwitz AF. Cell surface receptors for extracellular matrix molecules. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1987;3:179-205. [22]Singer II, Scott S, Kawka DW, et al. Cell surface distribution of fibronectin and vitronectin receptors depends on substrate composition and extracellular matrix accumulation. J Cell Biol. 1988;106(6):2171-2182. [23]Mosher DF. Assembly of fibronectin into extracellular matrix. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1993;3(2):214-222. [24]Yamada KM. Adhesive recognition sequences. J Biol Chem. 1991;266(20):12809-12812. [25]Brown EJ. Complement receptors, adhesion, and phagocytosis. Infect Agents Dis. 1992;1(2):63-70. [26]Remes A, Williams DF. Immune response in biocompatibility. Biomaterials. 1992;13(11):731-743. [27]Esmon CT. Thrombomodulin as a model of molecular mechanisms that modulate protease specificity and function at the vessel surface. FASEB J. 1996;9(10):946-955. [28]Plow EF, Herren T, Redlitz A, et al. The cell biology of the plasminogen system. FASEB J. 1995;9(10):939-945. [29]Jeon SI, Lee JH, Andrade JD, et al. Protein—surface interactions in the presence of polyethylene oxide: I. Simplified theory. J Colloids Interf Sci. 1991;142(1):149-158. [30]Jeon SI, Andrade JD. Protein—surface interactions in the presence of polyethylene oxide: II. Effect of protein size. J Colloids Interf Sci. 1991;142(1):159-166. [31]Milton Harris J. Poly(Ethylene Glycol) Chemistry: Biotechnical and Biomedical Applications. New York: Plenum Press, 1992: 385. [32]Llanos GR, Sefton MV. Does polyethylene oxide possess a low thrombogenicity? J Biomater Sci Polymer Ed. 1993;4(4): 381-400. [33]Amiji M, Park K. Surface modification of polymeric biomaterials with poly(ethylene oxide), albumin, and heparin for reduced thrombogenicity. J Biomater Sci Polymer Ed. 1993;4(3):217-234. [34]Fujimoto K, Tadokoro H, Ueda Y, et al. Polyurethane surface modification by graft polymerization of acrylamide for reduced protein adsorption and platelet adhesion. Biomaterials. 1993;14(6):442-448. [35]Uchida E, Uyama Y, Ikada Y. Grafting of Water-Soluble Chains Onto a Polymer Surface. Langmuir. 1994;10(2): 481-485. [36]Han DK, Ryu GH, Park DK, et al. Adsorption behavior of fibrinogen to sulfonated polyethyleneoxide-grafted polyurethane surfaces. J Biomater Sci Polymer Ed. 1993;4(5): 401-413. [37]Freij–Larsson C, Wesslén B. Grafting of polyurethane surfaces with poly(ethylene glycol). J Biomater Sci Polymer Ed. 1993;50(2):345-352. [38]Shoichet MS, Winn SR, Gentile FT, et al. Poly(ethylene oxide)-grafted thermoplastic membranes for use as cellular hybrid bio-artificial organs in the central nervous system. Biotech Bioeng. 1994;43(7):563-572. [39]Li S, Chatelier RC, Zientek P, et al. Covalent surface attachment of polysaccharides via bifunctional epoxides. Abstr Paper Am Chem Soc. 1995;209:305. [40]Gombotz WR, Guanghui W, Horbertt TA, et al. Protein adsorption to poly(ethylene oxide) surfaces. J Biomed Mater Res. 1991;25(12):1547-1562. [41]Merrill EW. Poly(ethylene oxide) star molecules: synthesis, characterization, and applications in medicine and biology. J Biomater Sci Polymer Ed. 1993;5(1-2):1-11. [42]Bergstrom K, Osterberg E, Holmberg K, et al. Effects of branching and molecular weight of surface-bound poly(ethylene oxide) on protein rejection. J Biomater Sci Polymer Ed. 1994;6(2):123-132. [43]Van Alstine JM, Burns NL, Riggs JA, et al. Electrokinetic characterization of hydrophilic polymer coatings of biotechnical significance. Colloid Surfaces. A. 1993;77(2): 149-158. [44]Burns NL, van Alstine JM, Harris JM. Poly(ethylene glycol) grafted to quartz: analysis in terms of a site-dissociation model of electroosmotic fluid flow. Langmuir. 1995;11(7): 2768-2776. [45]López GP, Ratner BK, Tidwell CD, et al. Glow discharge plasma deposition of tetraethylene glycol dimethyl ether for fouling-resistant biomaterial surfaces. J Biomed Mater Res. 1992;26(4):415-439. [46]Nojiri C, Olano T, Koyanagi H, et al. In vivo protein adsorption on polymers: visualization of adsorbed proteins on vascular implants in dogs. J Biomater SciPolym Ed. 1992;4(2):75-88. [47]Lee JH, Kopecek J, Andrade JD. Protein-resistant surfaces prepared by PEO-containing block copolymer surfactants. J Biomed Mater Res. 1989;23(3):351-268. [48]Amij MM, Park K. Analysis on the surface adsorption of PEO/PPO/PEO triblock copolymers by radiolabelling and fluorescence techniques. J Appl Polym Sci. 1994;52(4): 539-544. [49]Moghimi SM, Muir IS, Illum L, et al. Coating particles with a block co-polymer (poloxamine-908) suppresses opsonization but permits the activity of dysopsonins in the serum. Biochimicaet Biophysica Acta. 1993;1179(2):157-165. [50]Cinni E, Cavedagna D, Falsone G, et al. Numerical and functional modifications in platelets induced by polyester coated by a hydrophilic polymer. Biomaterials. 1993;14(8): 588-590. [51]Marchant RE, Yuan S, Szakalasgratzl G. Interactions of plasma proteins with a novel polysaccharide surfactant physisorbed to polyethylene. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 1994;6(6):549-564. [52]Ishihara K, Hanyuda H, Nakabayashi N. Synthesis of phospholipid polymers having a urethane bond in the side chain as coating material on segmented polyurethane and their platelet adhesion-resistant properties. Biomaterials. 1995;16(11):873-879. [53]Terlingen JG, Feijien J, Hoffman AS. Immobilization of surface active compounds on polymer supports using a gas discharge process. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 1992;4(1):31-33. [54]Tseng YC, Mcpherson T, Yuan CS, et al. Grafting of ethylene glycol-butadiene block copolymers onto dimethyl-dichlorosilane-coated glass by gamma-irradiation. Biomaterials. 1995;16(13):963-972. [55]Amiji M, Park K. Surface Modification by radiation-induced grafting of PEO/PPO/PEO triblock copolymers. J Colloid Inter Sci. 993;155(1):251-255. [56]Lasic DD. Sterically stabilized vesicles. Angew Chem. 1994;33:1685-1698. [57]Woodle MC, Lasic DD. Sterically stabilized liposomes. Biochimicaet Biophysica Acta. 1992;1113(2):171-199. [58]Cho CS, Kotaka T, Akaike T. Cell adhesion onto block copolymer Langmuir-Blodgett films. J Biomed Mater Res. 1993;27(2):199-206. [59]Uchida M, Tanizaki T, Oda T, et al. Control of surface chemical structure and functional property of Langmuir-Blodgett film composed of new polymerizable amphiphile with a sodium sulfonate. Macromolecules. 1991;24(11):3238-3243. [60]Lopez GP, Albers MW, Schreiber SL, et al. Convenient methods for patterning the adhesion of mammalian-cells to surfaces using SAMs of alkanethiolates on gold. J Am Chem Soc. 1993;115(13):5877-5878. [61]Prime KL, Whitesides GM. adsorption of proteins onto surfaces containing end-attached oligo (ethylene oxide): a model system using self-assembled monolayers. J Am Chem Soc. 1993;115(23):10714-10721. [62]Dimilla PA, Folkers JP, Biebuyck HA, et al. Wetting and protein adsorption of self-assembled monolayers of alkanethiolates supported on transparent films of gold. J Am Chem Soc. 1994;116(5):2225-2226. [63]Löfås S. Dextran modified self-assembled monolayer surfaces for use in biointeraction analysis with surface plasmon resonance. Pure Appl Chem. 1995;67(5):829-834. [64]Osterberg E, Bergstrom K, Holmberg K, et al. Protein-rejecting ability of surface-bound dextran in end-on and side-on configurations: comparison to PEG. J Biomed Mater Res. 1995;29(6):741-747. [65]Ferguson GS, Chaudhury MK, Biebuyck HA, et al. Monolayers on disordered substrates: self-assembly of alkyltrichlorosilanes on surface-modified polyethylene and poly(dimethylsiloxane). Macromolecules. 1993;26(22): 5870-5875. [66]Silver JH, Hergenrother RW, Lin JC, et al. Surface and blood-contacting properties of alkylsiloxane monolayers supported on silicone rubber. J Biomed Mater Res. 1995; 29(4):535-548. [67]O'Shea GM, Sun AM. Encapsulation of rat islets of Langerhans prolongs xenograft survival in diabetic mice. Diabetes. 1986;35(8):943-946. [68]Sawhney AS, Hubbell JA. Poly(ethylene oxide)-graft-poly (L-lysine) copolymers to enhance the biocompatibility of poly(L-lysine)-alginate microcapsule membranes. Biomaterials. 1992;13(12):863-870. [69]Desai NP, Sojomihardjo A, Yao Z, et al. Interpenetrating polymer networks of alginate and polyethylene glycol for encapsulation of islets of Langerhans. J Microencapsul. 2000;17(6):677-690. [70]Ishihara K, Inoue H, Kurita K, et al. Selective adhesion of platelets on a polyion complex composed of phospholipid polymers containing sulfonate groups and quarternary ammonium groups. J Biomed Mater Res.1994;28(11): 1347-1355. [71]Silver JH, Myers CW, Lim F, et al. Effect of polyol molecular weight on the physical properties and haemocompatibility of polyurethanes containing polyethylene oxide macroglycols. Biomaterials. 1994;15(9):695-704. [72]Lelah MD, Cooper SL. Polyurethanes in Medicine. Raton, Florida: CRC Press, 1986:225. [73]Brunstedt MR, Ziats NP, Robertson SP, et al. Protein adsorption to poly(ether urethane ureas) modified with acrylate and methacrylate polymer and copolymer additives. J Biomed Mater Res. 1993;27(3):367-377. [74]Grasel TG, Castner DG, Ratner BD, et al. Characterization of alkyl grafted polyurethane block copolymers by variable takeoff angle x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. JBiomed Mater Res. 1990;24(5):605-620. [75]Yu XH, Okkema AZ, Cooper SL. Synthesis and physical properties of poly(fluoroalkylether)urethanes. J Appl Polym Sci. 1990;41(7-8):1777-1795. [76]Yoon SC, Sung YK, Ratner BD. Surface and bulk structure of segmented poly(ether urethanes) with perfluoro chain extenders. 4. Role of hydrogen bonding on thermal transitions. Macromolecules. 1990;23(20):4351-4356. [77]Shin YC, Han DK, Kim YH, et al. Antithrombogenicity of hydrophilic polyurethane-hydrophobic polystyrene IPNs. II. In vitro and ex vivo studies. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 1994;6(3):281-296. [78]Matthews KH, Kodama M. The effect of microphase separated structures on the blood contacting properties of a series of linear segmented poly(etherurethaneurea) elastomers. Mater Sci Eng C Biom Mater Sensor Sys. 1994;2(1-2):51-59. [79]Tingey KG, Andrade JD. Probing surface microheterogeneity of poly(Ether Urethanes) in an aqueous environment. Langmuir. 1991;7(11):2471-2478. [80]Stauffer SR, Peppas NA. Poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogels prepared by freezing-thawing cyclic processing. Polymer. 1992;33(18):3932-3936. [81]Gu YJ, Inoue K, Shinohara S, et al. Xenotransplantation of bioartificial pancreas using a mesh-reinforced polyvinyl alcohol bag. Cell Transplant. 1994;3(Suppl 1):s19-21. [82]Fujimoto K, Minato M,Ikada Y. Poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogels prepared under different annealing conditions and their interactions with blood components. ACS Symp Ser. 1994;540(Chapter 20):228-242. [83]Chaikof EF, Merrill EW, Callow AD, et al. PEO enhancement of platelet deposition, fibrinogen deposition, and complement C3 activation.J Biomed Mater Res. 1992;26(9):1163-1168. |
| [1] | 李 黎, 马 力. 磁性壳聚糖微球固定化乳糖酶及其酶学性质[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(4): 576-581. |
| [2] | 刘 鋆, 杨 龙, 王伟宇, 周玉虎, 吴 颖, 卢 涛, 舒莉萍, 马敏先, 叶 川. 聚3-羟基丁酸酯4-羟基丁酸酯/聚乙二醇/氧化石墨烯组织工程支架的制备和性能评价[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(22): 3466-3472. |
| [3] | 周安琪, 唐渝菲, 吴秉峰, 向 琳. 骨膜组织工程设计:共性与个性的结合[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(22): 3551-3557. |
| [4] | 郎丽敏, 何 生, 姜增誉, 胡奕奕, 张智星, 梁敏茜. 导电复合材料在心肌梗死组织工程治疗领域的应用进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(22): 3584-3590. |
| [5] | 解 健, 苏俭生. 静电纺丝取向纳米纤维作为组织工程生物支架的优势与特征[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(16): 2575-2581. |
| [6] | 纪 琦, 喻正文, 张 剑. 3D打印金属基生物材料工艺和临床应用的问题与趋势[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(16): 2597-2604. |
| [7] | 宋涯含, 吴云霞, 范道洋. 基于VOSviewer生物医学领域3D打印的知识图谱分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(15): 2385-2393. |
| [8] | 钱楠楠, 张 潜, 杨 睿, 敖 俊, 章 涛. 间充质干细胞治疗脊髓损伤:细胞治疗及联合新药和生物材料[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(13): 2114-2120. |
| [9] | 罗雅馨, 毕浩然, 陈晓旭, 杨 琨. 细胞外基质与组织的再生与修复[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(11): 1785-1790. |
| [10] | 贾 巍, 张满栋, 陈维毅, 王晨艳, 郭 媛. 股骨假体材料对人工膝关节置换性能的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(10): 1477-1481. |
| [11] | 王 倩, 李 璐, 舒静媛, 董志恒, 靳友士, 王青山. 氧化锆基纳米羟基磷灰石功能梯度生物材料的微观形貌和物相分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(10): 1517-1521. |
| [12] | 杨亚楠, 李峻峰, 王 立, 刘恒全, 赖雪飞. 柠檬酸钙:一种有趣的有机钙生物医用材料[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(10): 1609-1615. |
| [13] | 王 刚, 李东辉, 白志明. 长段输尿管损伤替代治疗的方法、材料及修复重建的演变历程[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2020, 24(8): 1299-1305. |
| [14] | 李 黎, 马 力, 李 鹤. 磁性壳聚糖微球的制备及表征[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2020, 24(4): 577-582. |
| [15] | 唐萌萌, 陈和春, 谢宏晨, 张 瑜, 谭晓霜, 孙艺璇, 黄毅娜. 聚(L-丙交酯-ε-己内酯)/交联聚乙烯吡咯烷酮输尿管支架植入大鼠膀胱后的组织相容性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2020, 24(4): 583-588. |
Generally speaking, polymer materials used for in vivo implantation should have two basic properties, namely, the medical functionality and biocompatibility. In fact, these two properties also cover the other properties of the materials, such as the physical and mechanical properties, chemical stability, toxicity, formability and other requirements. Medical function refers to diagnostic or therapeutic effects achieved by a combination of materials and living tissues. The biocompatibility refers to the degree of mutual accommodation between materials and living tissues, and it contains two meanings: blood compatibility and tissue compatibility. Biocompatibility of biomaterials is the most important feature different from other materials, which is the fundamental basis for evaluating whether a material can be used in biomedicine. Therefore, biocompatibility is one of the central topics of biomaterials.
Data sources
1 此问题已知的信息:对于植入生物活体内的高分子材料,一般应具有两种基本性能,即医用功能性和生物相容性。 2 文章增加的新信息:在研制用于心血管组织工程的新型植(介)入型聚合物材料(表面)的研究中,应从聚合物生物材料的表面构建与生物反应行为方面(蛋白质吸附、细胞黏附中的生物识别、凝血与纤溶过程中的酶催化作用“瀑布模型”,以及生物材料的表面构建与蛋白质的表面吸附行为)归纳分析考察各种相应改性表面的生物相容性、血液相容性和细胞相容性。 3 临床应用的意义:致力于研究与开发新型可植(介)入性聚合物生物材料,以满足对心血管医疗器械的设计与制造需求。
在材料表面种植、培养细胞,制备适合细胞生长的高分子材料是实现材料良好生物相容性的根本途径。因此,适合细胞生长的生物材料研究,不仅对细胞-材料相互作用机制的深入理解有着积极的科学意义,而且对于为加速组织相容性和血液相容性材料临床应用的突破也有着巨大的价值。解决材料的生物相容性问题是生物材料在生物医学领域应用的关键。长期以来,在解决材料的生物相容性问题上,人们对材料表面的修饰研究得较多,如血液相容性材料的研制上,通常对材料进行表面分子设计,改善表面的亲硫水性、引入带电基团、负载生物活性物质等,以尽量减轻血栓的形成来提高材料的血液相容性。然而,处于生物系统中的材料由于接触到体液、有机大分子、酶、自由基、细胞等多种因素,其生物学环境极为复杂,表面修饰的方法对血液相容性的改善有限。 研制用于心血管组织工程的新型植(介)入型聚合物材料(表面)关键在于对聚合物生物材料生物功能性表面的构建以及对其相应生物相容性与内皮细胞相容性的研究。通过对心血管医疗用聚合物生物材料的种类与应用及其心血管医疗器件和可植入性软组织替代物的深入研究,可以发现表面与本体的差别则将体现在从表面向本体延伸的很多层分子上,而两种主要因素决定了其包括本体/表面差异及表面相分离在内的本体/表面行为,即表面能和分子运动性。如果考虑到对本体-表面的组成差异的理解,则还必须追加另以附加决定因素,即各组分的结晶行为。另外,使用变角XPS技术对改性剂端基在表面层不同深度处的含量进行了测量,并以之探讨端基与不同分子尺寸之PEO桥联之间的相互作用对表面构象的影响,可建立短链MSPEO改性物于水相界面典型的“PEO环形构象”模型。而表面涂层体系较之于本体共混体系,则强化了改性剂与基材间的不良相容性动力,同时弱化了“自迁移表面富集”的动力学阻力。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||